The digital entertainment landscape has fundamentally transformed over the past decade, with streaming platforms becoming the primary mode of content consumption globally. However, lurking in the shadows of this legitimate ecosystem exists a vast network of illegal movie distribution sites that continue to thrive despite mounting legal pressure and technological countermeasures. These platforms, including notorious names like iBomma, Movierulz, Tamilrockers, and Filmyzilla, have become household names in certain regions, particularly across India and Southeast Asia.
Ever wondered how websites like iBomma, Movierulz, Tamilrockers, and keep running despite being illegal?
The persistence of these illegal streaming platforms represents one of the most significant challenges facing the global entertainment industry today [5]. Recent data reveals that piracy websites attracted a staggering 216 billion visits globally in 2024, with individual popular sites like iBomma and Movierulz drawing between 20-40 million visitors monthly [2][3]. The United States leads global piracy traffic with 26.7 billion visits, followed closely by India with 17.6 billion visits, highlighting the truly international scope of this phenomenon [1][2].
What makes these operations particularly fascinating from a business perspective is their ability to generate substantial revenue streams while operating entirely outside legal frameworks [6]. Industry estimates suggest that the global piracy ecosystem generates approximately $2.34 billion annually, with individual sites potentially earning millions through sophisticated monetization strategies [7][8]. This revenue generation occurs through multiple channels, including advertising networks, subscription services, cryptocurrency mining, and affiliate marketing partnerships [9][10].
The complexity of these operations extends far beyond simple content hosting [11]. Modern piracy sites employ advanced content delivery networks, mirror site architectures, and bulletproof hosting services to maintain operations across multiple jurisdictions [12][13]. They frequently change domain extensions from .com to .to, .cx, .ru, and other country-specific domains to evade law enforcement actions [14][15]. This cat-and-mouse game with authorities has created an entire underground economy with its own technological innovations and business practices [16].
Global piracy website traffic by country showing the United States and India as the top sources
The impact on legitimate content creators and distributors cannot be overstated [5]. In India alone, the film industry loses an estimated Rs 20,000 crore annually to piracy, affecting everyone from major studios to independent filmmakers [17][18]. This massive revenue loss translates to reduced investment in new projects, fewer job opportunities for industry professionals, and ultimately, a diminished quality and quantity of content available to consumers [19][20].
What Are Pirated Sites Like iBomma, Movierulz, etc.?
Pirated content platforms represent sophisticated digital ecosystems designed to distribute copyrighted material without authorization from content owners [21][3]. These websites function as comprehensive entertainment portals, offering users access to movies, television shows, web series, and other premium content that would typically require payment through legitimate channels [11]. Unlike legitimate streaming services that invest billions in content licensing and original productions, piracy sites operate by circumventing these costs entirely, allowing them to offer content at no charge to end users [22].
The landscape of movie piracy sites is particularly dominated by platforms focusing on Indian regional content, with Telugu, Tamil, Hindi, and Kannada films representing the largest categories of pirated material [4][23]. iBomma, for instance, has established itself as the primary destination for Telugu movie enthusiasts, offering everything from the latest blockbusters to classic films in various quality formats [3]. Similarly, Movierulz has built a reputation for providing rapid access to new releases across multiple Indian film industries, often uploading content within hours of theatrical release [21].
Tamilrockers, perhaps the most notorious of these platforms, has been operating since 2011 and has evolved from a simple bootleg recording network into a sophisticated content distribution system [24]. The site’s impact on the Tamil film industry has been so significant that it regularly issues “challenges” before major film releases, threatening to upload pirated versions on release day [4]. This brazen approach has made Tamilrockers a symbol of the broader piracy problem facing the Indian entertainment industry [24].
Distribution of pirated content types showing TV shows as the most pirated category
The popularity of these platforms in Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities, as well as among overseas Indian communities, stems from several factors [3][23]. Primary among these is the limited availability of legitimate streaming options in smaller markets, where major OTT platforms may not offer comprehensive regional content libraries [25]. Additionally, the cost of multiple streaming subscriptions can be prohibitive for users in these markets, making free alternatives particularly attractive [26].
The technological sophistication of modern piracy sites often surprises users expecting crude, amateur operations [11]. Many of these platforms feature polished user interfaces, advanced search functionality, multiple download options, and even recommendation engines similar to those found on legitimate streaming services [27]. This professional presentation helps legitimize the experience for users who might otherwise be deterred by obviously illicit operations [28].
Content categorization on these sites typically follows industry standards, with movies organized by language, genre, release year, and quality [3][21]. Users can typically choose from multiple file formats and resolutions, ranging from low-quality cam recordings suitable for mobile viewing to high-definition rips that rival legitimate streaming quality [29]. This flexibility in content delivery has been crucial to their widespread adoption across diverse user bases with varying technical capabilities and bandwidth limitations [30].
The global reach of these platforms extends far beyond their countries of origin [23]. Indian piracy sites, for example, serve significant audiences in the United States, Canada, Australia, and other countries with large Indian diaspora populations [1]. This international dimension complicates enforcement efforts, as sites often operate across multiple jurisdictions with varying copyright laws and enforcement capabilities [16].
How Do They Get the Content?
The content acquisition methods employed by piracy sites represent a complex network of sources ranging from insider access to sophisticated technological circumvention [31][30]. Understanding these methods is crucial for comprehending how sites like iBomma and Movierulz maintain their extensive content libraries and rapid upload schedules [32].
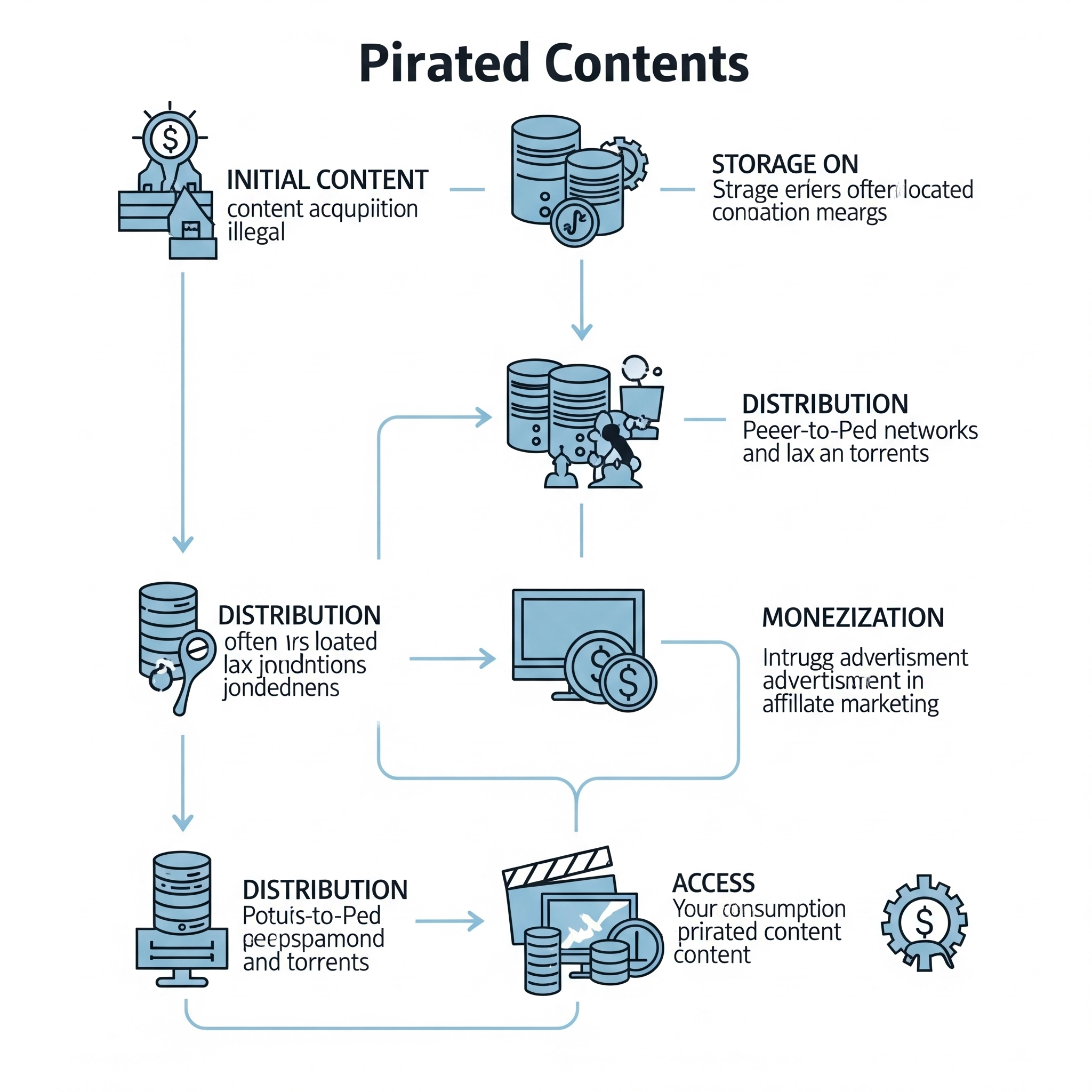
An infographic illustrating the operations behind pirated content websites, from content acquisition to monetization and user access.
Theater-based recording, commonly known as “camming,” remains one of the most traditional and persistent sources of pirated content [29][33]. This method involves individuals using concealed recording devices in movie theaters to capture films during their initial theatrical run [31]. The resulting “cam” recordings, while often of poor quality due to ambient theater noise and visual obstructions, serve as the first available pirated versions of new releases [29]. Industry data suggests that cam recordings contribute approximately 15-20% of total movie piracy, making it a significant source despite technological countermeasures [32].
Professional camming operations have evolved considerably from amateur recordings made with handheld devices [31]. Modern cam operations often involve multiple individuals working in coordination, with some focusing on video recording while others handle audio capture using separate devices [33]. These recordings are then combined and processed to improve quality before distribution [29]. Some operations even employ theater employees who provide inside access or overlook recording activities in exchange for compensation [4].
Post-production leaks represent another significant source of high-quality pirated content [34][30]. These leaks can occur at various stages of the content creation process, from editing facilities to distribution networks [11]. Insiders with access to master copies or work prints may sell or distribute content before its official release, sometimes resulting in pirated versions becoming available even before theatrical premieres [31]. The entertainment industry has implemented increasingly sophisticated watermarking and tracking systems to identify the sources of such leaks, but determined insiders continue to find ways to circumvent these measures [30].
The rise of streaming platforms has created new opportunities for content piracy through what industry experts term “screen recording” and “stream ripping” [30][35]. Unlike traditional downloading methods, these techniques involve capturing content as it plays on legitimate streaming platforms [30]. Advanced users employ software tools that can bypass basic copy protection measures implemented by streaming services, allowing them to create high-quality digital copies of content [35]. Some operations use multiple accounts and automated systems to systematically capture and redistribute content from platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and regional OTT services [34].
OTT platform vulnerabilities have become increasingly exploited by sophisticated piracy operations [34][35]. These vulnerabilities can include weak DRM implementations, insecure content delivery networks, or compromised user credentials [36]. Content Delivery Network (CDN) leeching has emerged as a particularly sophisticated method, where pirates gain unauthorized access to the infrastructure used by legitimate streaming services to deliver content to users [35][37]. This method allows pirates to obtain content in the same high quality that legitimate users receive, without the quality degradation associated with screen recording [35].
Insider sources within the entertainment industry continue to pose significant challenges for content protection [4][34]. These sources can include employees at production companies, distribution networks, theater chains, or even streaming platforms themselves [32]. The Tamilrockers operation, for example, has been linked to a network of contributing members across the globe who upload content in exchange for payment based on download metrics [4]. This decentralized model makes it extremely difficult for law enforcement to identify and prosecute all participants in the network [24].
The speed at which new content appears on piracy sites often indicates the involvement of insider sources or highly sophisticated technical operations [34][38]. Major releases frequently appear on piracy sites within hours of their official premiere, sometimes even before they become available on legitimate streaming platforms [31]. This rapid turnaround suggests either direct access to distribution copies or extremely efficient recording and processing operations [30].
International content sharing networks have also developed among piracy sites, allowing them to exchange content and reduce individual operational risks [15]. Sites specializing in different regional markets often share resources, with a site focused on Telugu content potentially providing material to sites serving Tamil or Hindi markets in exchange for content from those regions [23]. This collaborative approach helps maintain the comprehensive content libraries that make these sites attractive to users [28].
Why Do People Visit These Sites?
The motivations driving millions of users to piracy sites despite legal alternatives represent a complex interplay of economic, accessibility, and behavioral factors [26][25]. Understanding these motivations is essential for comprehending why sites like iBomma and Movierulz continue to attract massive audiences even as legitimate streaming options proliferate [1].
Economic considerations rank among the primary drivers of piracy site usage [26][39]. For many users, particularly in developing markets, the cumulative cost of multiple streaming subscriptions can represent a significant portion of disposable income [25]. A typical household wanting access to comprehensive content might need subscriptions to Netflix, Amazon Prime, Disney+, and multiple regional OTT platforms, potentially costing $50-100 monthly [40]. In contrast, piracy sites offer unlimited access to content from all these platforms at no cost [6].
The fragmentation of content across multiple streaming platforms has created what industry analysts term “subscription fatigue” [39][40]. Unlike the early days of streaming when Netflix or a single platform could satisfy most viewing needs, today’s landscape requires multiple subscriptions to access desired content [39]. This fragmentation has inadvertently driven users toward piracy sites that aggregate content from all platforms in a single location [28]. Users increasingly view piracy sites as solving a legitimate problem created by the streaming industry’s business model [25].
Accessibility and availability issues further contribute to piracy site usage [23][25]. Many users in regions outside major markets find that legitimate streaming platforms either don’t serve their geographic area or offer limited content libraries compared to what’s available in primary markets [41]. For Indian diaspora communities, for example, accessing the latest Telugu or Tamil films through legitimate channels may be impossible or significantly delayed [23]. Piracy sites fill this gap by providing immediate access to regional content regardless of geographic location [3].
The timing advantage offered by piracy sites represents another crucial factor [31][28]. While legitimate platforms often operate under complex release windows that delay content availability, piracy sites typically offer new releases immediately upon theatrical premiere or even earlier [38]. For users eager to stay current with popular culture or participate in social media discussions about new releases, this timing difference can be decisive [26].
User experience factors also play a significant role in piracy site adoption [28][27]. Many users report that piracy sites offer superior search functionality, better content organization, and more flexible viewing options compared to some legitimate platforms [25]. The ability to download content for offline viewing, choose from multiple quality options, and access content without creating accounts or remembering passwords appeals to users seeking convenience [3][21].
The lack of registration requirements on most piracy sites eliminates barriers that legitimate platforms erect [3][26]. Users can access content immediately without providing personal information, payment details, or email addresses [21]. This anonymity appeals not only to users concerned about privacy but also to those who simply want immediate access without navigating signup processes [27].
Technological factors also influence user behavior patterns [26][42]. In regions with limited internet bandwidth or unreliable connections, the ability to download content for later viewing becomes crucial [3]. Many piracy sites offer multiple file size and quality options, allowing users with bandwidth constraints to choose appropriate formats [30]. Legitimate streaming platforms, by contrast, often require consistent high-speed connections for optimal viewing experiences [40].
Social and cultural factors contribute to the normalization of piracy site usage in certain communities [26][20]. In regions where intellectual property concepts are less established or where piracy is widely practiced, using these sites carries less social stigma [23]. Peer recommendations and social media sharing often introduce new users to piracy sites, creating viral growth patterns [42].
The perceived quality advantage of pirated content in some cases also drives usage [5][30]. Users seeking content in original languages with subtitles, or specific regional versions not available on legitimate platforms, often turn to piracy sites that offer more comprehensive language and subtitle options [3]. Additionally, piracy sites sometimes offer content in higher quality formats than legitimate platforms provide in certain regions [35].
Educational and research motivations account for a subset of piracy site usage [43]. Students, researchers, and film enthusiasts seeking access to rare or educational content not available through legitimate channels may turn to piracy sites as research tools [5]. While this represents a smaller segment of users, it highlights the gap between academic needs and commercial content availability [20].
The Hidden Business Model – How They Make Money
The revenue generation mechanisms of piracy sites represent a sophisticated underground economy that has evolved to become remarkably profitable despite operating entirely outside legal frameworks [8][9]. The business model underlying sites like iBomma, Movierulz, and similar platforms involves multiple revenue streams that collectively generate substantial income for operators [6][7].
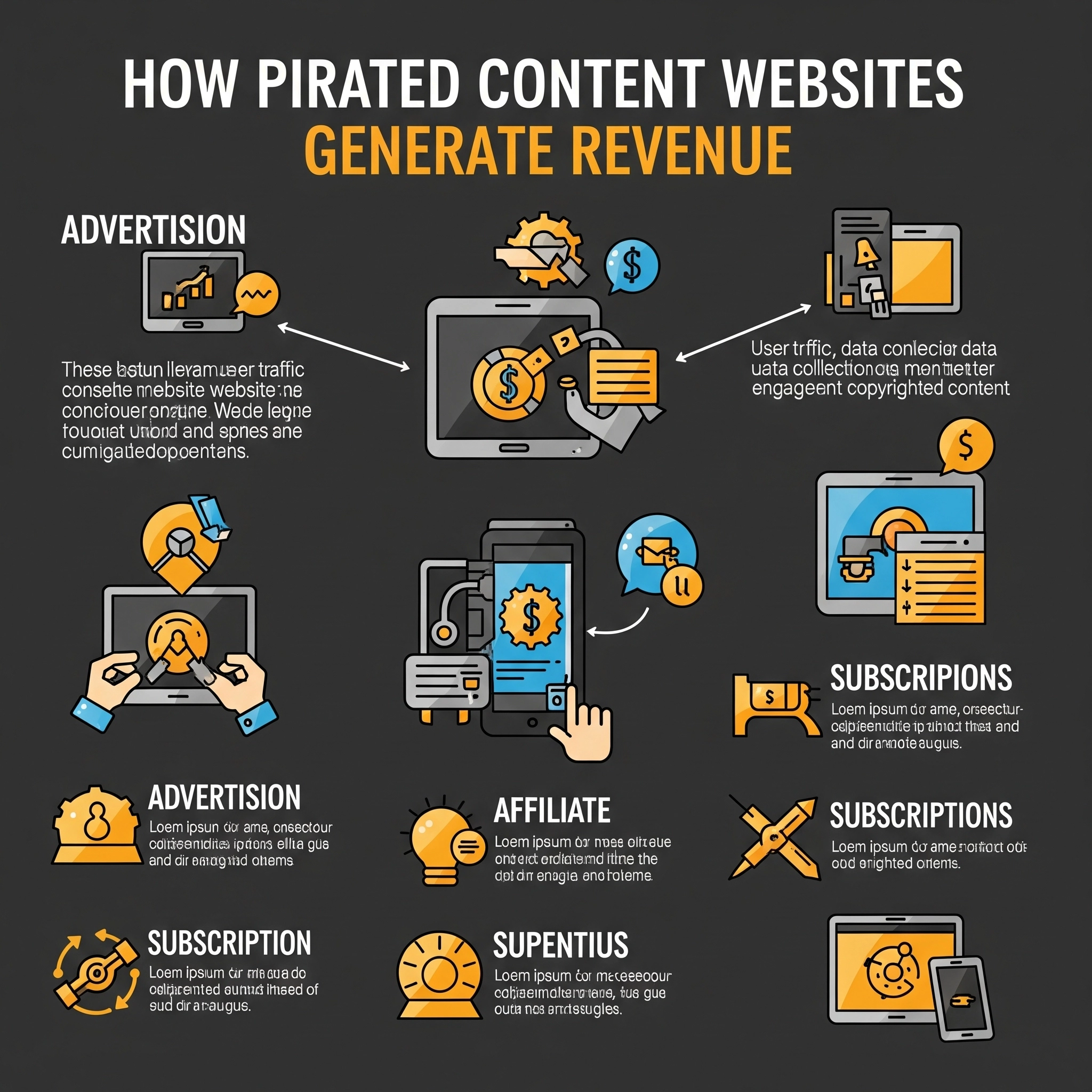
Revenue breakdown showing how piracy websites generate income, with advertising being the primary source
Online advertising serves as the primary revenue source for most piracy sites, accounting for approximately 57% of total income according to industry analyses [8][10]. Unlike legitimate websites that work with reputable advertising networks, piracy sites typically partner with lower-tier ad networks that are less concerned about content legitimacy [9]. These networks often serve advertisements for questionable products and services, including gambling sites, adult content, fake pharmaceutical products, and potentially fraudulent services [6][8].
The advertising ecosystem surrounding piracy sites operates on significantly higher payment rates than legitimate advertising [9]. Advertisers willing to place ads on illegal sites often pay premium rates because they’re targeting audiences that traditional advertising channels cannot reach [8]. This creates a mutually beneficial relationship where piracy sites earn higher revenue per impression while advertisers access otherwise unreachable demographics [10].
Pop-up and redirect-based advertising represents another significant revenue stream [6][9]. Users attempting to access content on piracy sites often encounter multiple pop-up windows, forced redirects, and interstitial advertisements before reaching their desired content [44]. Each of these interactions generates revenue for site operators, with some networks paying based on clicks regardless of whether users complete desired actions [8]. This model explains why piracy sites often feature aggressive advertising that legitimate sites would never implement [10].
Subscription services have emerged as an increasingly important revenue source for piracy sites [6][45]. Contrary to popular belief, many piracy sites offer premium subscription tiers that provide ad-free experiences, faster download speeds, and priority access to new content [21]. These subscriptions typically cost significantly less than legitimate streaming services while offering access to content from multiple platforms [39]. The use of cryptocurrency payments for these subscriptions has grown substantially, with blockchain analysis revealing approximately $24 million in cryptocurrency payments to piracy sites between 2019 and 2023 [45].
Affiliate marketing partnerships generate substantial revenue through partnerships with VPN services, file hosting platforms, and other digital services [10][8]. Piracy sites often promote VPN services to users concerned about legal consequences, earning commissions on each subscription sale [9]. Similarly, they partner with file hosting services and download managers, creating revenue streams while providing tools that enhance the user experience [6].
Cryptocurrency mining scripts, often called “crypto-jacking,” represent a more covert revenue generation method [46][45]. Many piracy sites embed JavaScript code that uses visitors’ computer processing power to mine cryptocurrencies without explicit consent [46]. While individual mining returns may be modest, the massive traffic volumes on popular piracy sites can generate significant cumulative revenue [44]. The Pirate Bay famously experimented with this approach, though user backlash led to its discontinuation [46].
Direct content sales and premium downloads provide additional revenue streams [6][4]. Some piracy operations sell high-quality downloads or early access to content through private channels [21]. The Tamilrockers network, for example, reportedly compensates contributors based on the download popularity of their uploads, creating an incentive structure that encourages continued participation [4].
Malware distribution, while controversial, represents another revenue source for some piracy operations [44][42]. Operators may include malware in download packages or use the massive traffic to their sites to distribute potentially unwanted programs [20]. This practice is particularly concerning given that malware infections affect approximately 59% of users visiting piracy sites [44][42].
The sophistication of these revenue models often surprises observers expecting crude operations [7][6]. Many piracy sites employ advanced analytics to optimize ad placement, A/B test different monetization strategies, and maximize revenue per visitor [10]. Some operations reportedly generate millions of dollars annually through these combined revenue streams [9].
Geographic arbitrage plays a crucial role in the profitability of piracy operations [12][13]. By hosting infrastructure in countries with lower operational costs while serving audiences in higher-income markets, operators can maximize profit margins [16]. This geographic distribution also complicates law enforcement efforts while reducing operational expenses [47].
The economics of piracy site operations become clear when considering their minimal content acquisition costs compared to legitimate platforms [22][7]. While Netflix or Amazon Prime must pay billions for content licensing, piracy sites obtain the same content through illegal means at essentially zero cost [39]. This fundamental cost advantage allows them to generate substantial profits even with relatively modest advertising revenue [8][9].
Why Is It Illegal? And Still, How Do They Survive?
The illegal nature of movie piracy sites stems from fundamental violations of intellectual property laws that exist in virtually every jurisdiction worldwide [19][43]. These platforms directly contravene multiple legal frameworks, including national copyright acts, international treaties, and digital rights legislation [48][17]. Understanding both the legal basis for prohibition and the methods sites use to evade enforcement illuminates the ongoing cat-and-mouse game between piracy operators and authorities [18][49].
Copyright infringement represents the primary legal violation committed by piracy sites [19][48]. The Copyright Act of 1957 in India, similar to copyright legislation worldwide, grants exclusive rights to content creators to control the reproduction, distribution, and public display of their works [17][18]. When sites like iBomma or Movierulz host and distribute movies without authorization, they violate these exclusive rights [21][3]. The scope of violation extends beyond simple hosting to include facilitating access, providing search functionality, and actively promoting pirated content [19][20].
Criminal penalties for copyright infringement can be severe across jurisdictions [19][43]. In the United States, copyright violations can result in fines up to $250,000 and imprisonment for up to five years for first-time offenders [43]. Repeat offenders face up to ten years imprisonment [19]. India’s copyright law provides for imprisonment up to three years and fines, with enhanced penalties under the recently amended Cinematograph Act of 2023 [17][18]. The establishment of nodal officers empowered to order content takedowns within 48 hours represents a significant escalation in enforcement capabilities [18].
The international scope of piracy operations complicates enforcement efforts significantly [16][47]. Modern piracy sites typically operate across multiple jurisdictions, hosting content in one country, managing operations from another, and serving users globally [12][13]. This geographic distribution exploits differences in national copyright laws, enforcement capabilities, and international cooperation agreements [16]. Sites often migrate their operations to countries with weaker intellectual property enforcement or limited extradition treaties [47][13].
Domain manipulation represents one of the most common survival strategies employed by piracy sites [14][15]. When authorities block or seize a primary domain, operators simply migrate to new domain extensions or entirely different web addresses [27][16]. A single piracy operation might maintain dozens of mirror sites across different top-level domains, ensuring that users can always find working links [15]. The rapid proliferation of new generic top-level domains has made this strategy even more effective [14].
Bulletproof hosting services provide crucial infrastructure for piracy operations [12][13]. These hosting providers, often located in jurisdictions with minimal legal oversight, explicitly cater to clients operating illegal or questionable services [13]. Bulletproof hosts typically ignore takedown requests, resist legal cooperation, and employ technical measures to protect their clients’ operations [12]. The rise of bulletproof hosting has significantly complicated law enforcement efforts to permanently shut down piracy sites [13].
The use of Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) and proxy networks adds additional layers of protection [35][16]. Piracy sites often distribute their content across multiple CDNs, making it difficult to completely disable access even when individual servers are compromised [37]. Proxy networks allow sites to mask their true hosting locations and provide users with alternative access points when primary domains are blocked [15][16].
Cryptocurrency adoption has enhanced the anonymity and financial security of piracy operations [45][46]. Traditional payment systems can be monitored and blocked by financial institutions cooperating with law enforcement [43]. Cryptocurrency transactions, while not completely anonymous, provide significantly greater privacy and are much more difficult for authorities to trace or intercept [45]. The growth in cryptocurrency payments to piracy sites demonstrates the effectiveness of this approach [46].
Cloud infrastructure and distributed hosting models have made piracy operations more resilient [35][12]. Rather than relying on single servers that can be easily shut down, modern piracy sites often distribute their operations across multiple cloud providers and hosting services [13]. This distribution makes it virtually impossible to completely eliminate a site’s presence without coordinated international action [16].
Legal jurisdiction shopping allows piracy operators to exploit regulatory arbitrage [47][16]. By carefully selecting hosting locations, domain registrations, and operational centers in different countries, operators can make enforcement extremely complex and time-consuming [12]. Even when one jurisdiction takes action, operators can quickly shift to others with more favorable legal environments [13].
Recent enforcement successes demonstrate both the potential and limitations of anti-piracy efforts [38][49]. The shutdown of Fmovies in 2024, described as the world’s largest piracy operation with over 6.7 billion visits, required international cooperation between Vietnamese authorities and Hollywood studios [38][50]. However, within days of the shutdown, mirror sites and successor operations began appearing [49]. The Alliance for Creativity and Entertainment (ACE) reported shutting down over 50 major piracy operations in 2024, yet new sites continue to emerge [49][51].
The technical sophistication of modern piracy operations often exceeds the capabilities of enforcement agencies [11][35]. Operators employ advanced security measures, encryption, and obfuscation techniques that require specialized technical knowledge to counter [12][13]. The skills gap between operators and enforcement officials creates significant challenges for effective action [16].
The Real Danger of Visiting These Websites
The security risks associated with visiting piracy websites extend far beyond legal consequences, creating a dangerous digital environment that threatens users’ personal data, financial security, and device integrity [44][42]. Research consistently demonstrates that piracy sites pose significantly higher malware risks than other categories of potentially dangerous websites, with infection rates reaching 59% compared to 57% for adult content sites and 53% for gambling platforms [44][42].
Security threats and risks users face when visiting piracy websites
Malware distribution represents the most immediate and widespread threat facing piracy site users [44][20]. Unlike legitimate websites that invest heavily in security infrastructure, piracy sites often lack proper security measures and may actively participate in malware distribution as an additional revenue stream [42][20]. Users downloading content from these sites frequently encounter trojans, viruses, ransomware, and spyware hidden within media files or bundled with download software [43][44]. The sophistication of these attacks has evolved considerably, with some malware specifically designed to target users seeking pirated content [20].
Ransomware attacks have become increasingly common through piracy site vectors [44][43]. Cybercriminals specifically target piracy site users because they represent valuable targets who have demonstrated willingness to download and install software from untrusted sources [42]. Once infected, ransomware encrypts users’ files and demands payment for restoration, often demanding hundreds or thousands of dollars [20]. The anonymous nature of cryptocurrency payments preferred by ransomware operators makes recovery extremely difficult [43].
Data theft and privacy violations occur frequently on piracy platforms [44][42]. Many sites employ tracking scripts that monitor user behavior, collect personal information, and build detailed profiles for sale to third parties [20]. The lack of privacy protections means that browsing histories, search queries, and downloaded content lists may be recorded and potentially used for blackmail or other malicious purposes [44]. Some sites have been discovered selling user data to marketing companies or criminal organizations [42].
Financial fraud schemes specifically target piracy site users through various deceptive practices [44][6]. Fake premium subscription offers, fraudulent payment processing, and cryptocurrency scams are common on these platforms [20][45]. Users attempting to pay for “premium” access often find their payment information stolen and used for unauthorized transactions [42]. The underground nature of these operations makes fraud recovery virtually impossible [43].
Phishing attacks frequently originate from piracy site advertising networks [44][9]. Users clicking on advertisements or pop-ups may be directed to fake websites designed to steal login credentials, personal information, or financial data [20]. These attacks often mimic legitimate services like banks, streaming platforms, or social media sites, making them difficult to detect [42]. The high-traffic nature of piracy sites makes them attractive platforms for phishing operations [44].
Cryptocurrency mining scripts, while less immediately dangerous than malware, can significantly impact device performance and electricity costs [46][44]. Many piracy sites embed JavaScript code that uses visitors’ computers to mine cryptocurrencies without consent or notification [46]. This unauthorized use of computing resources can slow devices, increase electricity bills, and potentially damage hardware through excessive usage [44]. The Pirate Bay’s experimentation with cryptocurrency mining highlighted the prevalence of this practice [46].
Legal consequences for users vary significantly by jurisdiction but can include substantial fines and criminal prosecution [19][43]. While enforcement against individual users remains inconsistent, several countries have implemented increasingly aggressive prosecution policies [17][48]. Internet service providers in many jurisdictions now monitor user activity and may suspend services or report suspected piracy to authorities [19]. The growth of automated copyright enforcement systems increases the likelihood of detection [18].
Poor content quality and fake downloads plague piracy sites, leading to user frustration and potential security risks [20][29]. Many downloads contain corrupted files, incorrect content, or embedded malware disguised as popular movies or shows [44]. The lack of quality control means users may download gigabytes of useless data while exposing themselves to security threats [42]. Some sites deliberately offer fake downloads to maximize advertising exposure or deliver malware payloads [20].
Device performance degradation often results from visiting piracy sites due to aggressive advertising, malware infections, and resource-intensive scripts [44][46]. Users frequently report slower internet connections, increased pop-up advertisements, and general system instability after visiting these platforms [42]. The cumulative effect of multiple security threats can render devices nearly unusable and require professional cleaning or complete reinstallation of operating systems [20].
Network security compromises can affect entire households or organizations when infected devices spread malware through local networks [44][43]. Corporate networks are particularly vulnerable when employees access piracy sites on work devices, potentially exposing sensitive business data and violating workplace policies [42]. The interconnected nature of modern networks means that a single infected device can compromise multiple systems [20].

Illustration depicting the risks of piracy websites
Adult content exposure and inappropriate advertising represent additional concerns, particularly for younger users [27][44]. Piracy sites frequently display explicit advertisements and may redirect users to adult content sites without warning [6]. Parents often discover that children attempting to access popular movies have been exposed to inappropriate material through piracy site advertising networks [42]. The unregulated nature of these platforms means no age verification or content filtering protections exist [20].
The psychological impact of security breaches and fraud can be substantial and long-lasting [44][42]. Users who fall victim to identity theft, financial fraud, or blackmail schemes often experience significant stress and anxiety [43]. The violation of privacy and security can affect victims’ willingness to engage with digital services and may require extensive time and effort to resolve [20]. Recovery from serious security incidents can take months or years and cost thousands of dollars [44].
Why You Should Never Use Pirated Sites
The comprehensive analysis of piracy site operations, revenue models, and associated risks reveals a clear conclusion: the temporary benefit of free content access cannot justify the substantial personal, legal, and ethical costs involved [5][40]. While these platforms may appear to offer an attractive alternative to paid streaming services, the reality encompasses significant dangers that extend far beyond individual users to impact entire creative industries and economies [19][17].
The financial support provided to criminal enterprises through piracy site usage represents a fundamental ethical concern [8][9]. Every visit to these platforms, regardless of whether users click advertisements or make purchases, contributes to revenue streams that fund illegal operations [6][7]. The estimated $2.34 billion annual revenue generated by the global piracy ecosystem directly supports criminal networks that engage in various illegal activities beyond content theft [1][45]. Users who consider themselves law-abiding citizens inadvertently become participants in these criminal enterprises through their patronage [20].
The devastating impact on creative industries and individual creators demands serious consideration [5][17]. The Indian film industry alone loses approximately Rs 20,000 crore annually to piracy, representing thousands of jobs and countless creative projects that never receive funding [18][52]. Independent filmmakers and smaller production companies suffer disproportionately, as they lack the resources to absorb revenue losses that major studios might weather [5][20]. Every pirated view represents lost income that could have supported actors, directors, writers, technicians, and countless other industry professionals [19].
Supporting legitimate content platforms ultimately benefits consumers through improved content quality, innovation, and service reliability [40][53]. Legal streaming services invest billions in original content creation, technological improvements, and user experience enhancements [39]. Revenue from legitimate subscriptions directly funds new productions, creates employment opportunities, and drives technological innovation in content delivery [5]. The competitive landscape among legal platforms has led to remarkable improvements in content quality, accessibility features, and viewing options [25][28].
The security risks associated with piracy sites create ongoing vulnerabilities that legitimate alternatives completely avoid [44][42]. Legal streaming platforms invest heavily in cybersecurity, privacy protection, and user safety measures [40]. Premium services offer secure payment processing, robust privacy protections, and customer support for technical issues [39]. The peace of mind that comes with using legitimate services eliminates concerns about malware, data theft, identity fraud, and legal consequences [43][20].
Economic considerations often cited as justifications for piracy actually favor legitimate alternatives when properly analyzed [53][25]. The comprehensive cost of using piracy sites includes potential malware remediation, legal fees, identity theft recovery, and device replacement expenses [44][43]. A single serious security incident can cost significantly more than years of legitimate streaming subscriptions [42]. Additionally, the fragmented and unreliable nature of piracy sites often leads users to waste substantial time searching for working links and quality content [20].
Legal streaming platforms provide superior user experiences across multiple dimensions [25][40]. Professional customer support, reliable streaming quality, comprehensive search functionality, and personalized recommendations create viewing experiences that piracy sites cannot match [28][39]. The convenience of synchronized viewing across devices, offline download options, and family sharing features add substantial value beyond content access [21]. These platforms also offer accessibility features for users with disabilities, reflecting their commitment to inclusive content consumption [40].
The growth and improvement of legal alternatives have eliminated many traditional justifications for piracy [53][25]. Multiple streaming services now offer free, ad-supported tiers that provide substantial content libraries without subscription costs [26]. Regional OTT platforms have expanded their offerings to include comprehensive local content catalogs [3]. YouTube, Amazon Prime Video, and other services offer rental options for new releases at reasonable prices [40]. The combined effect of these developments means that legal alternatives exist for virtually every content consumption need [39].
Supporting content creators through legitimate channels enables continued innovation and artistic development [5][19]. Subscription and rental revenues fund new technologies, experimental content formats, and emerging creator programs [39]. The success of legal platforms has enabled unprecedented investment in diverse voices, international content, and niche programming that might never have found traditional distribution channels [25]. Consumers who choose legal alternatives directly contribute to this creative ecosystem and cultural diversity [5].
The legal streaming landscape continues evolving to address consumer concerns about cost and accessibility [53][40]. Bundle packages, family plans, and promotional pricing make comprehensive content access increasingly affordable [39]. Competition among platforms drives continuous improvements in pricing, content quality, and user experience [25]. Government and industry initiatives are expanding broadband access and reducing barriers to legal content consumption in underserved markets [18].
Individual consumer choices collectively shape the future of entertainment content and distribution [5][39]. The success of legal platforms validates business models that compensate creators fairly while providing convenient consumer access [40]. Conversely, continued support for piracy undermines these sustainable models and may eventually lead to reduced content quality, higher prices, or restrictive distribution practices [19]. The choice between supporting legal or illegal content distribution represents a vote for the type of entertainment ecosystem consumers want to create [20][5].
The comprehensive evidence demonstrates that using pirated sites exposes users to substantial risks while undermining the creative industries that produce the content they enjoy [44][5]. Legal alternatives provide superior experiences, better security, and direct support for continued content creation [40][39]. The ethical choice is clear: support creators and protect yourself by choosing legitimate streaming platforms over piracy sites [19][18].
The future of entertainment depends on consumers making informed decisions that support sustainable, legal content distribution models that benefit creators, consumers, and society as a whole [5][40]. In an era of abundant legal alternatives, there is simply no justification for the risks and ethical compromises inherent in using piracy sites [25][39]. Choose legal platforms, support content creators, and protect your digital security by avoiding the dangerous world of movie piracy altogether [18][43].
⁂


В последние годы бесплатные юридические консультации в Москве стали набирать популярность . Причиной этого является увеличившаяся необходимость в юридической поддержке . Профессионалы в области юриспруденции предлагают свои услуги на безвозмездной основе.
Бесплатные юридические консультации должны быть доступны каждому желающему. Обратиться за юридической помощью может любой гражданин, независимо от его финансового положения . Это также поможет снизить число правонарушений .
Процесс получения бесплатной консультации обычно несложен . Обычно достаточно записаться на консультацию к специалисту . Некоторые юристы проводят консультации дистанционно.
В заключение, бесплатные юридические консультации в Москве представляют собой значимую помощь для населения . Правовая поддержка способствует повышению правосознания граждан . Не стесняйтесь обращаться за помощью, если это необходимо .
полный текст https://twosidenews.com/%d0%ba%d0%be%d0%bd%d1%81%d1%83%d0%bb%d1%8c%d1%82%d0%b0%d1%86%d0%b8%d1%8f-%d0%b1%d0%b5%d0%b7-%d0%be%d0%bf%d0%bb%d0%b0%d1%82%d1%8b-%d0%bf%d0%be%d0%bb%d1%83%d1%87%d0%b8%d1%82%d0%b5-%d0%bf%d0%be%d0%bc/